No magic - just our painstaking joint work on the site
11 ways to improve the work of categories pages on an e-commerce website from the SEO point of view
According to Sam Underwood’s article
Suppose you have long been engaged in the search promotion of sites. In that case, you probably know that the opinion of SEO professionals and UX designers regarding filling pages of categories may not coincide. Usually, optimizers want to fill them as much as possible with texts and links. UX specialists set other priorities: increasing transitions to product cards are much more important.
However, if you choose the right strategy, you can keep the selling nature of the categories and, at the same time, use content that will help users decide on ordering. We suggest considering ways to improve the category pages taking into account the interests of potential buyers.
On the importance of categories
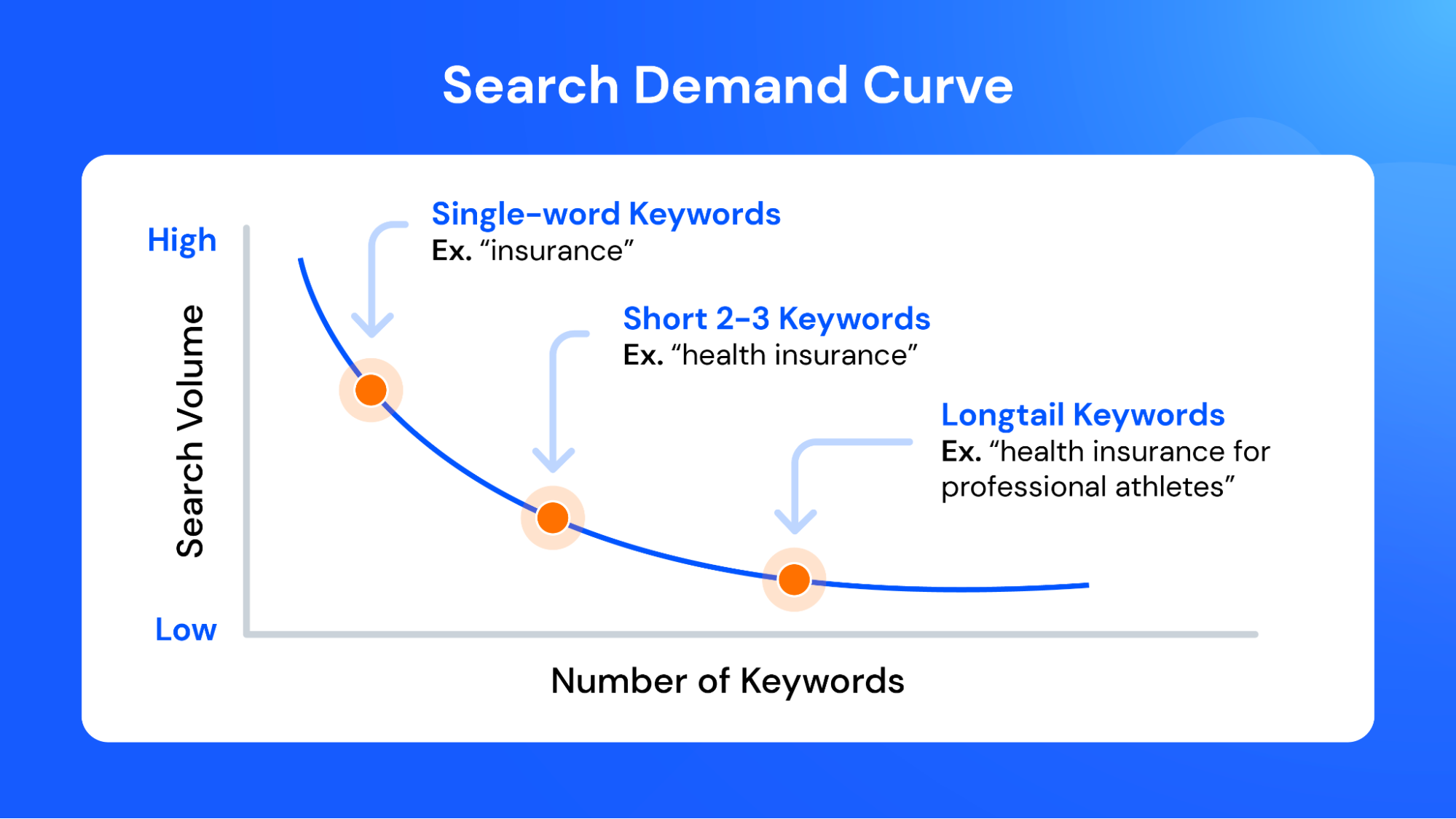
Optimizing category pages is an effective way to obtain search traffic on short-tail keywords, on which most competitors want to get into SERPs Top.
Grouping items and creating category pages allows:
- Familiarize users with products through easy navigation;
- Effectively allocate PageRank between subcategories and pages by internal linking;
- Organize content for better perception of website architecture by users and search engines.
It is important to remember that long-tail keywords can promote categories.
Types of category pages
There’s only two of them.
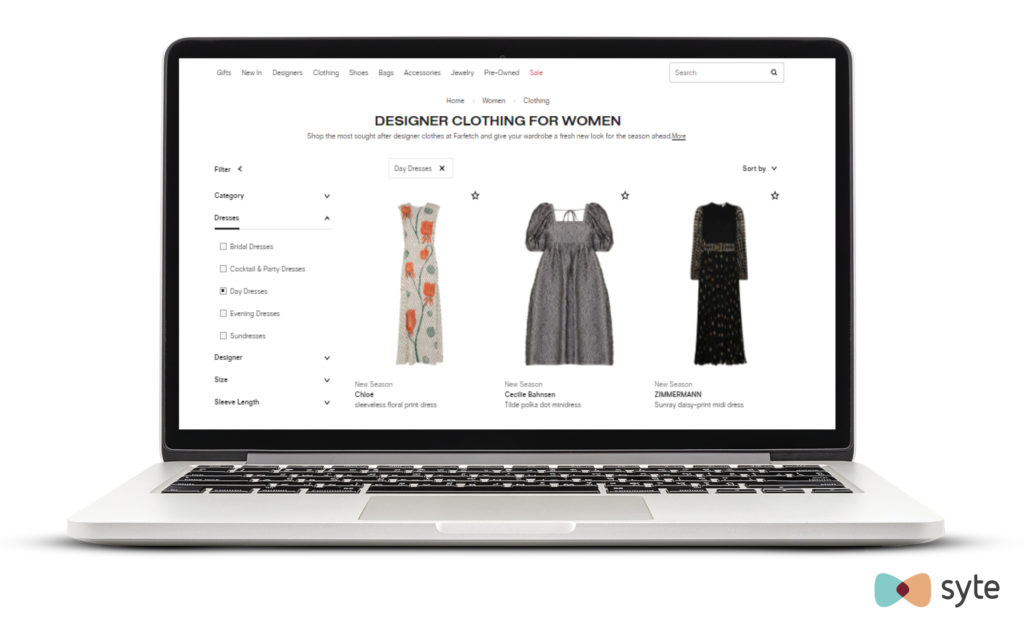
1. Category Listing Page (CLP). In many top online stores, their list is displayed in the site's top menu.
CLP example on ASOS:
CLP ranks with different keywords without being tied to the needs and tastes of potential buyers. All types of products are available to users according to the query.
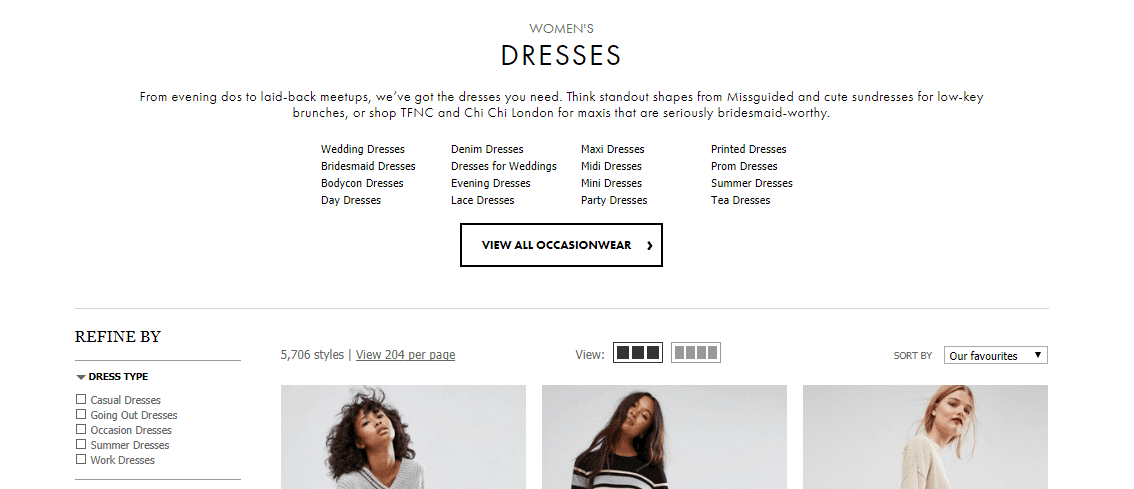
2. Product Listing Page (PLP). This type of page specifies the user’s wishes. If a potential buyer is interested in men’s black boots, he will be shown only such offers.
PLP example on ASOS:
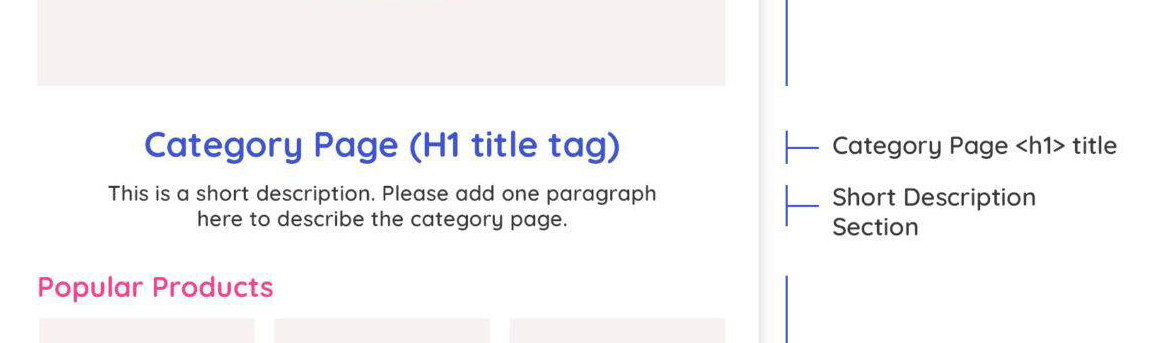
Main page elements
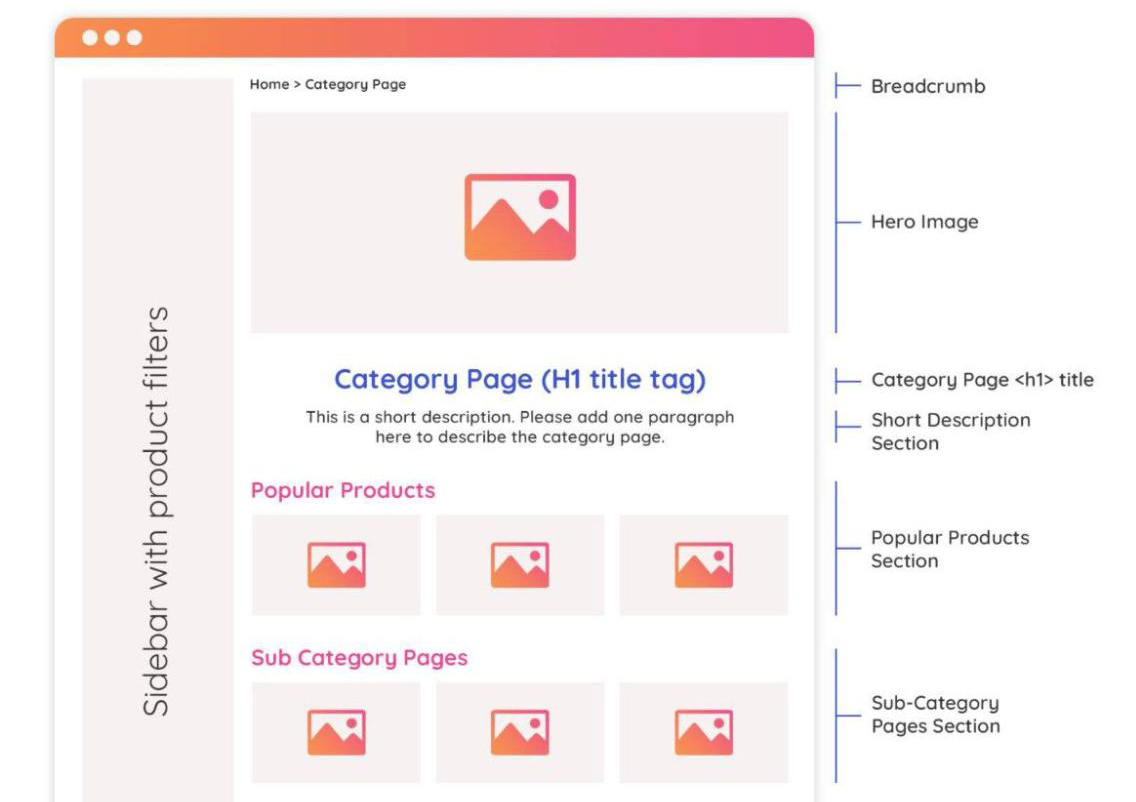
A typical category page looks like a PLP and contains:
- H1;
- text description;
- product list that can be placed on several pages;
- filters (brand, color, price, etc.).
The elements that buyers and search engines like can be much more. To better understand the possibilities of their placement on the site, let us give an example page layout.
Let us consider these paragraphs further. After analyzing and developing each block, you can significantly improve the perception of your site's category pages by target audience and search engine.
1. Helpful content
The content on the website helps the user make the right choice. At the same time, if you are describing the category of “rings,” do not tell the story of the appearance of accessories since this information is unlikely to be of interest to a potential buyer. The category page should provide answers to the following questions:
- What metal is the jewelry made of?
- Which diamonds are used in the jewelry: artificial or natural?
- What is the peculiarity of brand products? Why should they be preferred?
- What accessories are in trend now, and which style to choose?
The description under H1 should be brief - about 30-60 words. The nuances can be told in the general content block or FAQ section.
The presence of helpful content makes the online store more user-friendly and improves the ranking. In addition, texts, photos, and videos answer questions of users that do not know the product and help them make choices. Pages that contain only a link to goods are difficult to take high positions in SERP.
Expert content is essential, but one should not overdo it and publish long reads by overloading pages with information. It is sufficient to briefly answer the questions that influence the decision.
2. Classification
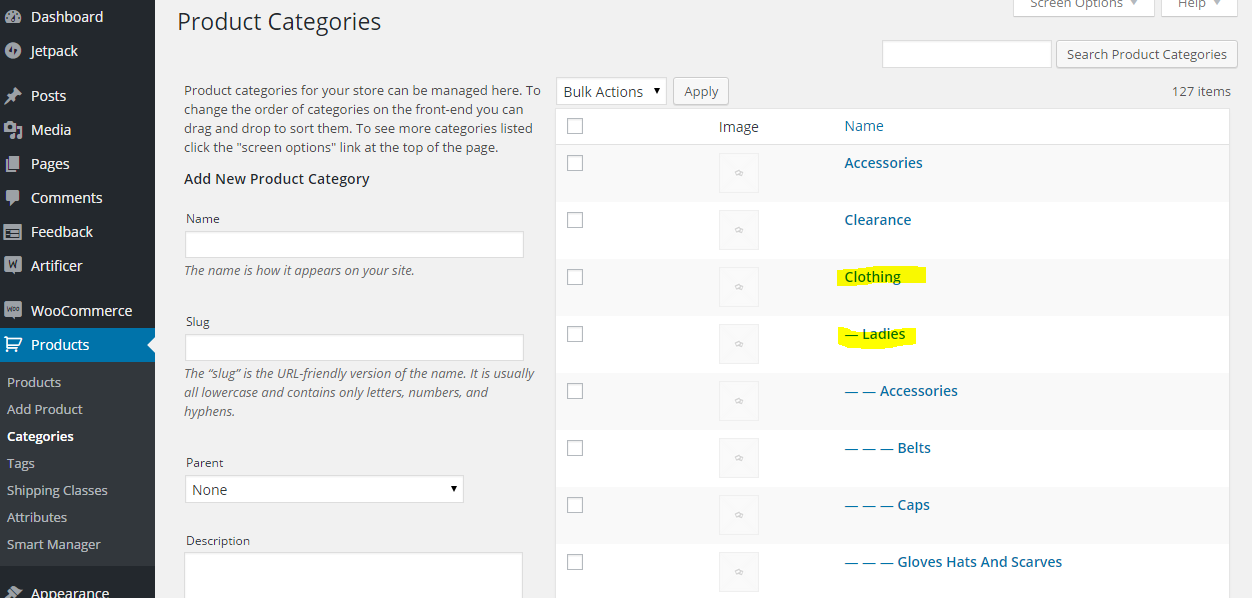
The structure of most e-commerce resources is based on logical links between the primary and subordinate pages.
Here is how this principle is implemented in the site structure on WooCommerce:
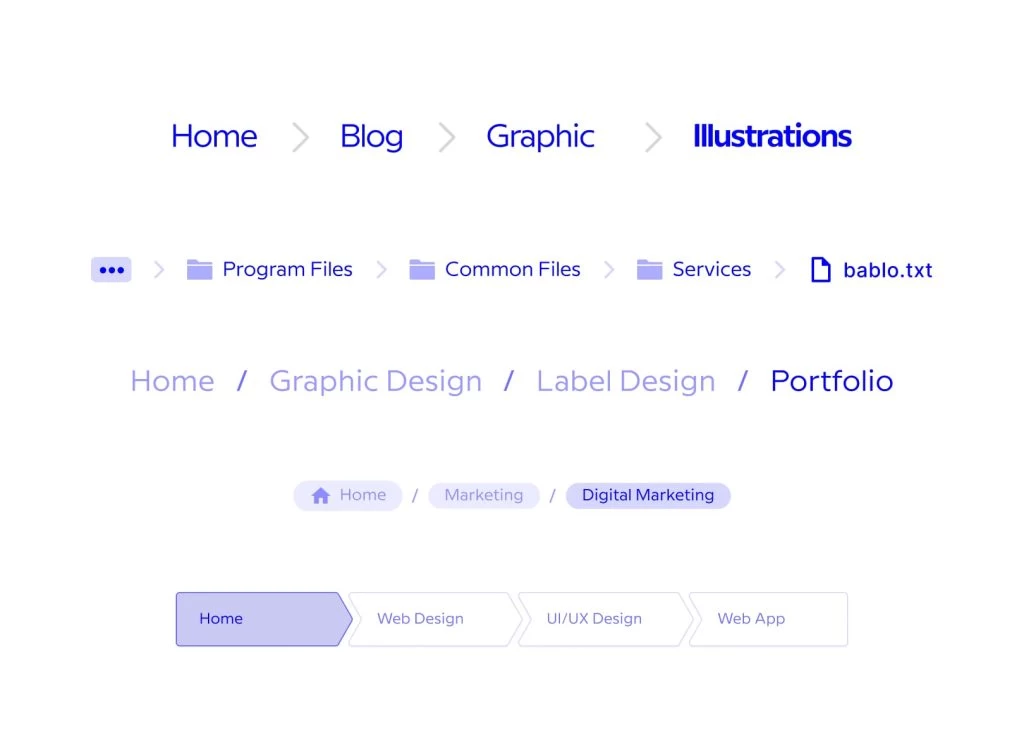
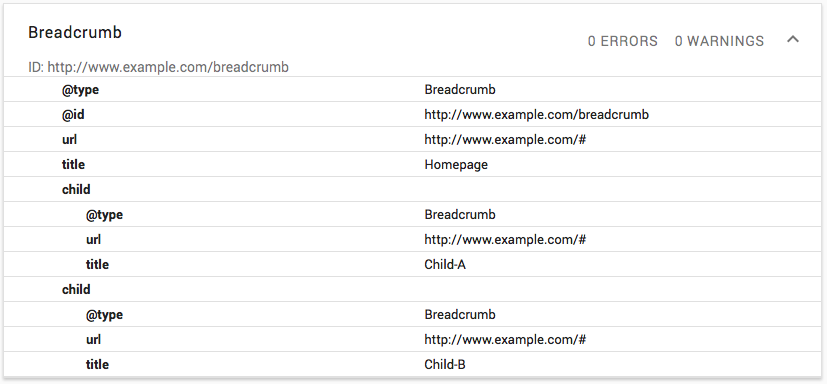
Organization of categories and creation of logical hierarchy helps to output bread crumbs properly.
An illustrative example can be found on the SEO Toolbelt website:
Breadcrumbs do not allow visitors to get lost on the website, showing the section in which they are at a certain moment. They allow you to distribute PageRank and improve the SERP results.
At the same time, many UX specialists do not like working with breadcrumbs because they:
- take up a lot of room;
- sometimes are not aesthetic;
- lead users to categories, not product cards, where conversion usually happens.
Do not overuse this element. Search bots can accept keywords in breadcrumbs for spam, eventually decreasing conversion and worsening the indexing of pages.
By the way, the location of breadcrumbs does not play an essential role in SEO. Therefore, if necessary, they can be placed at the bottom of the page.
3. Internal links
To improve the site's user-friendliness, behavioral factors and indexing, sections and products should be linked to other pages that might interest the audience. For e-commerce resources, combining automated and manual link management is advisable.
Manual linking on the online store's pages takes a lot of effort and time. You can use special plugins for automatization. Redirection from one page to another can be based on the following:
- hierarchy, parent/child categories;
- similar categories.
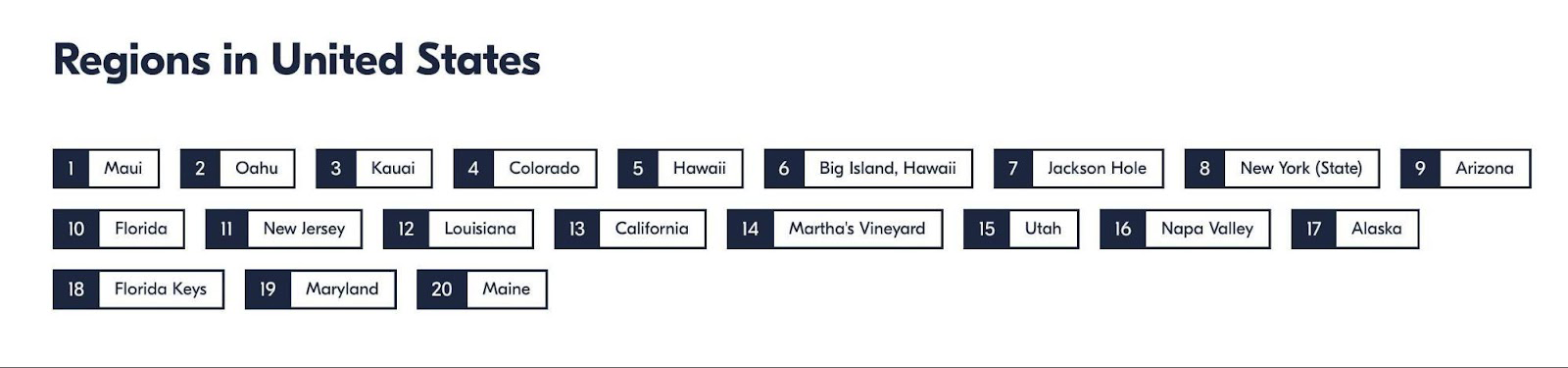
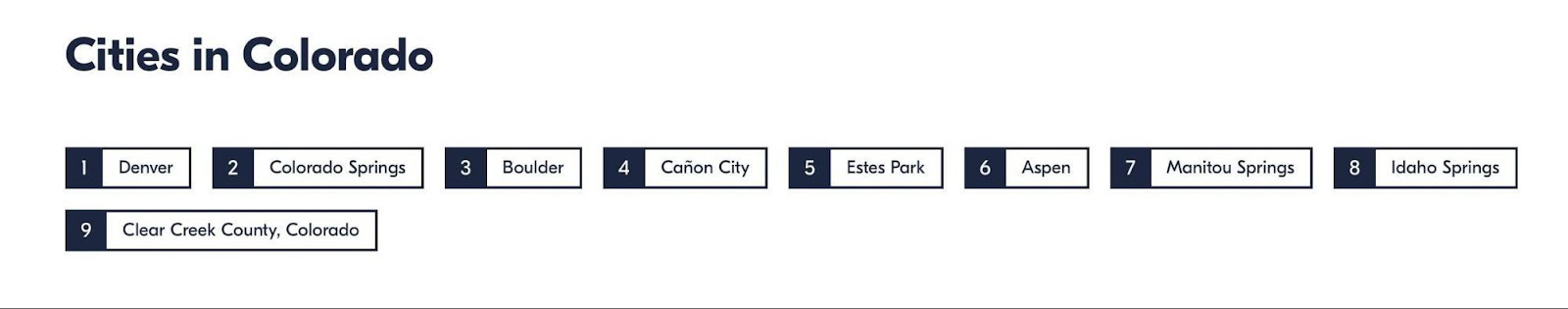
For example, the GetYourGuide site, on “Things to Do” in the US section, has a block of links that lead to state subsections lower down the page:
When choosing Colorado, this site will show the cities of the respective region at the same place.
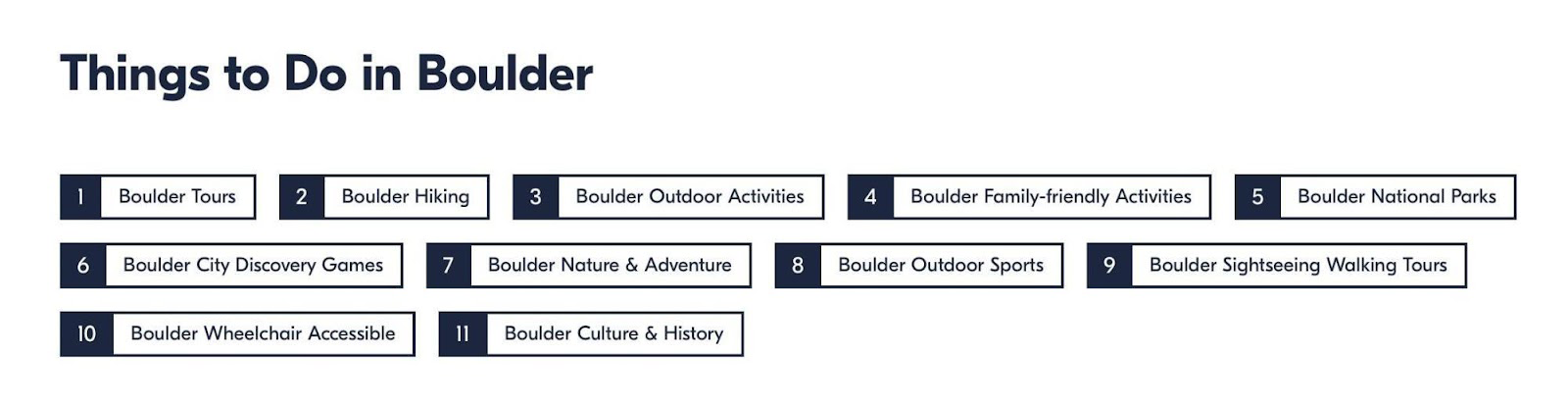
By selecting Boulder, for example, you will see links to the activity categories.
We see that the program understands the structure’s hierarchy and automates connections. The appropriate chain is built in breadcrumbs.
This solution allows the following:
- avoid orphan pages, after moving to which users leave the resource;
- automatically link a new subcategory to the specified parent one;
- users and search engines to understand resource structure.
Thus, we automatically have the pyramidal site structure, in which the parent pages link to subcategories.
Related categories are connected the same way. However, automated linking will not be suitable for all resources.
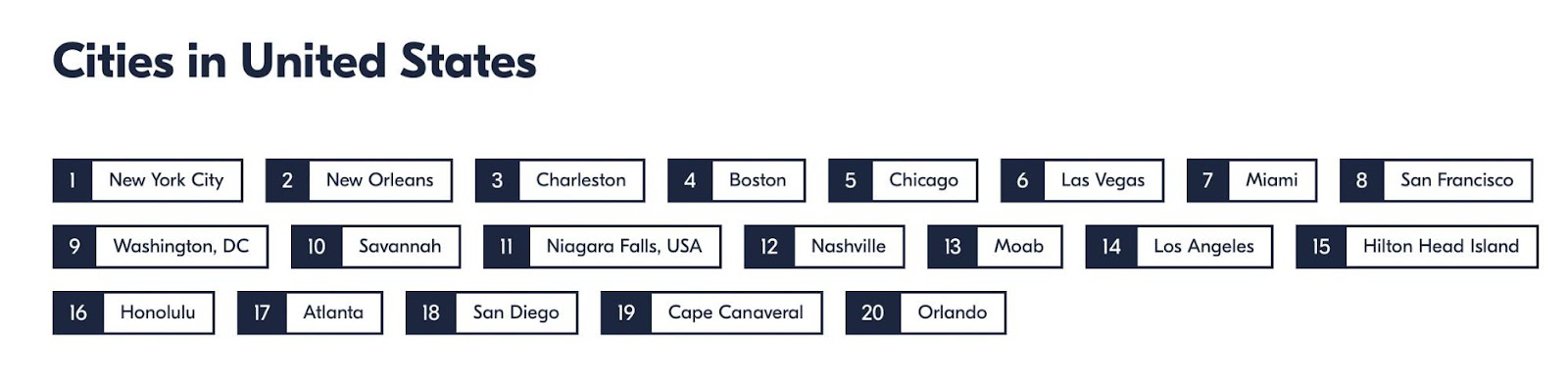
In the following example, we see that Boulder’s GetYourGuide page has links to other popular cities:
The program accesses the site database to get links, receives information about the main category, and displays child subsections.
A high search opportunity page mustn't be lost in a complex structure. To prevent this, we advise linking popular categories to those in the hierarchy closer to the homepage.
4. Pagination and linking to products
The primary purpose of category pages is to provide links to specific products. You need to know some crucial nuances to make transitions as effective as possible.
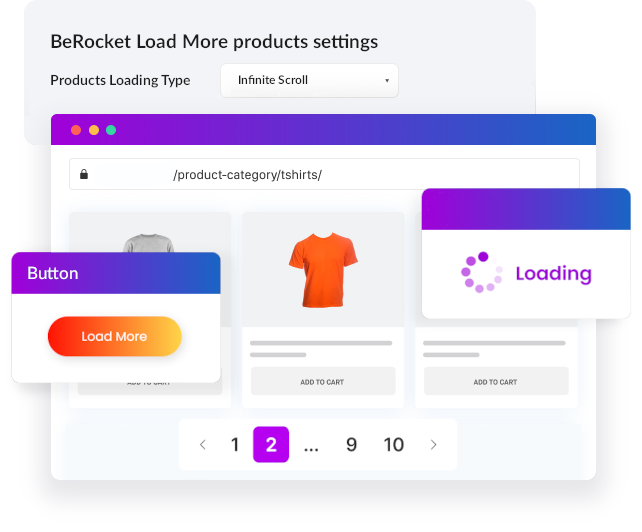
Indeed, it is advisable to show users popular products rather than relying on all products with pagination. On the British brand Sports Direct website, you can see that the section page contains links not to the entire range but only to TOP sales.
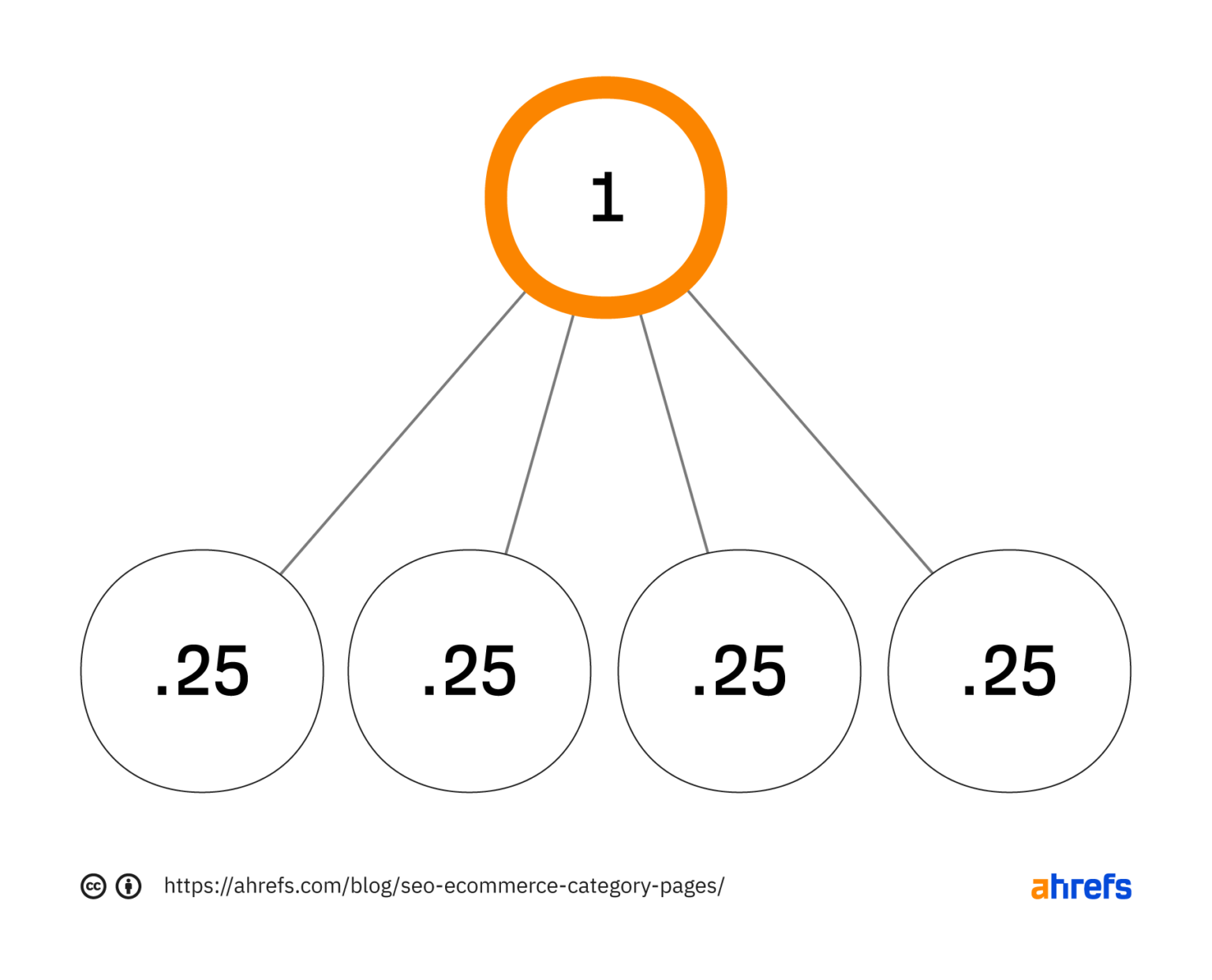
This solution is convenient for customers and allows you to distribute PageRank among these URLs and improve their ranking.
This approach works much more efficiently than linking a large number of less popular products. In the latter case, the product cards will receive less PageRank and take a lower position in SERP.
Create the “Watch all” option to view other products when placing links to bestsellers. In this case, PageRank will be distributed evenly between linked pages. Keep in mind that the implementation of the option implies a high loading speed of product offers.
In addition, do not include a full assortment in the pagination: it is better to provide the user with a choice of specific options that best satisfy the search query. For example, the “women’s dresses” section on ASOS contains 176 pages.
Whenever a site refers to a page of the “women’s dresses” category, it dilutes PageRank. Last-page items are unlikely to be ranked. It is, therefore, worth focusing PageRank on product cards with more specific parameters. For example, if the user reaches 20 pages, you need to help him narrow the search by adding subsections with color, style, etc. This approach is also convenient from the UX point of view.
It is up to you to decide which pagination strategy is appropriate for your website - linking to multiple component pages or sequential linking like ASOS. Testing will assess the effectiveness of both approaches.
5. Long-tail categories
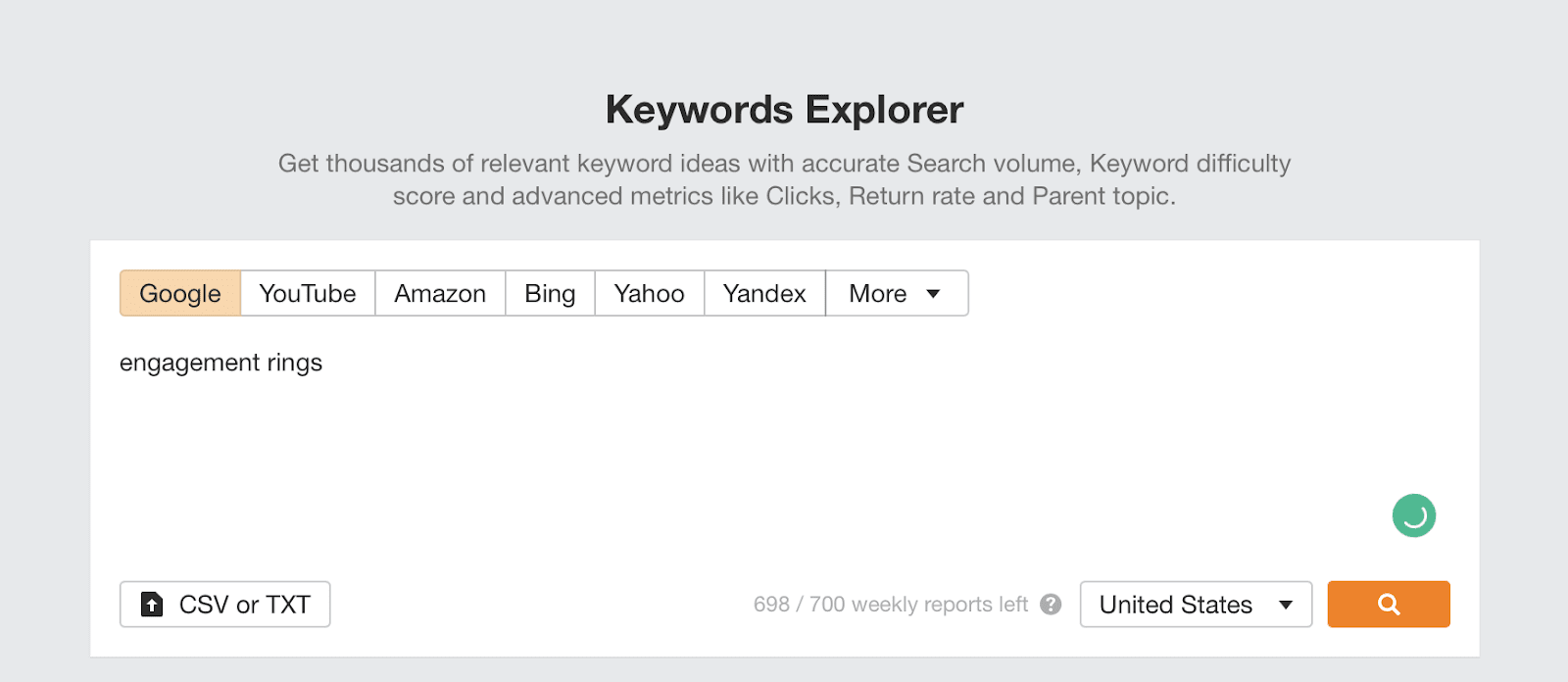
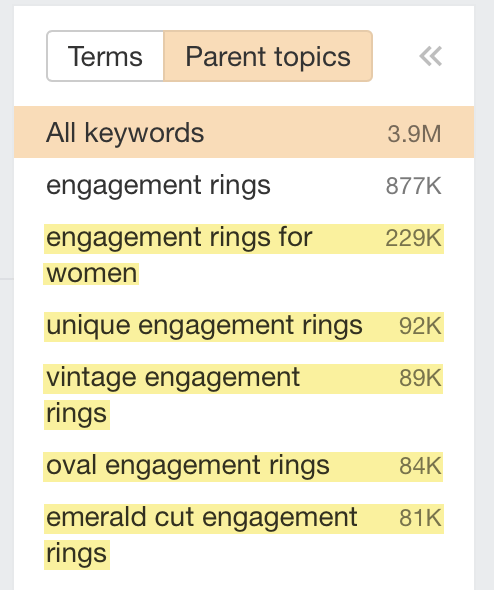
Creating pages displayed by long-tail queries within general categories is an effective and well-known optimization tactic. Use Ahrefs Keywords Explorer to select keywords.
Start by entering the query on which the general category is ranked, for example, “rings.”
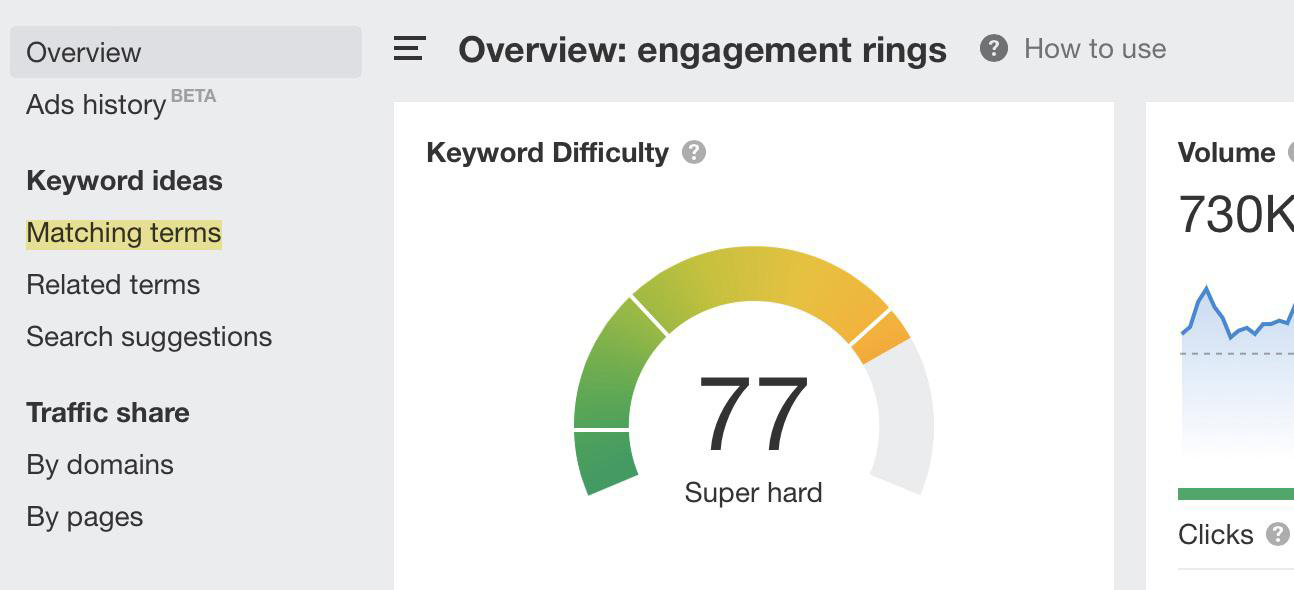
Next, select the Matching terms tab.
In the following left sidebar, select Parent topics. The tool will display a list of keywords with similar search results.
In the following left sidebar, select Parent topics. The tool will display a list of keywords with similar search results.
You can select long-tail keywords from this list and use them in subcategories. Creating new sections allows you to cover the “ring” topic better and rank on a wide pool of queries.
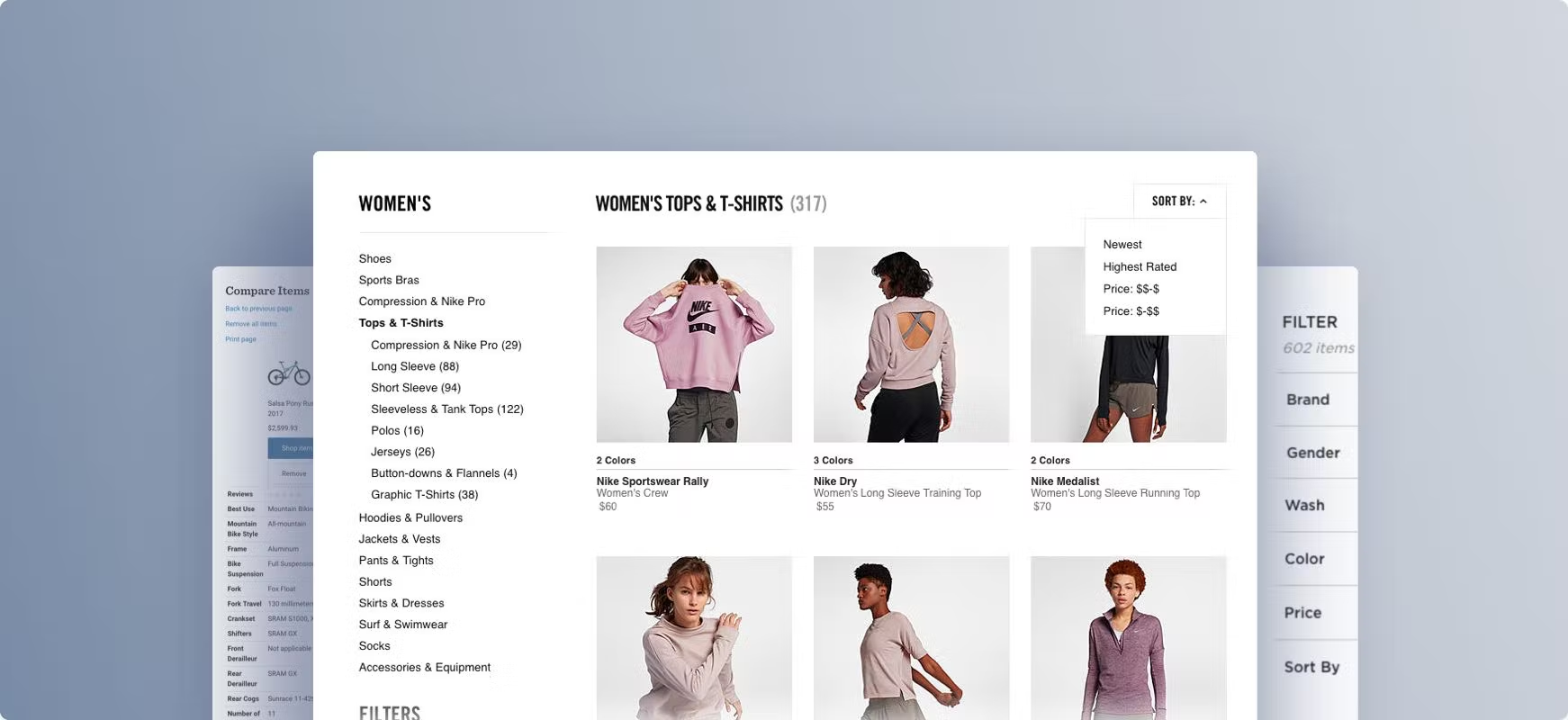
6. Faceted navigation strategy
Faceted navigation, or “filters,” is a crucial point to consider in listing categories.
Here is how this option looks on the Nike website:
According to SEO, you should consider several essential points in the process of creating filters:
- the need to close faceted links from Google indexing to prevent excessive spending of the crawling budget;
- closing low-value facets from indexing.
We recommend creating faceted navigation using AJAX, not adding <a href>-links, and specifying alternative crawl paths to important facets.
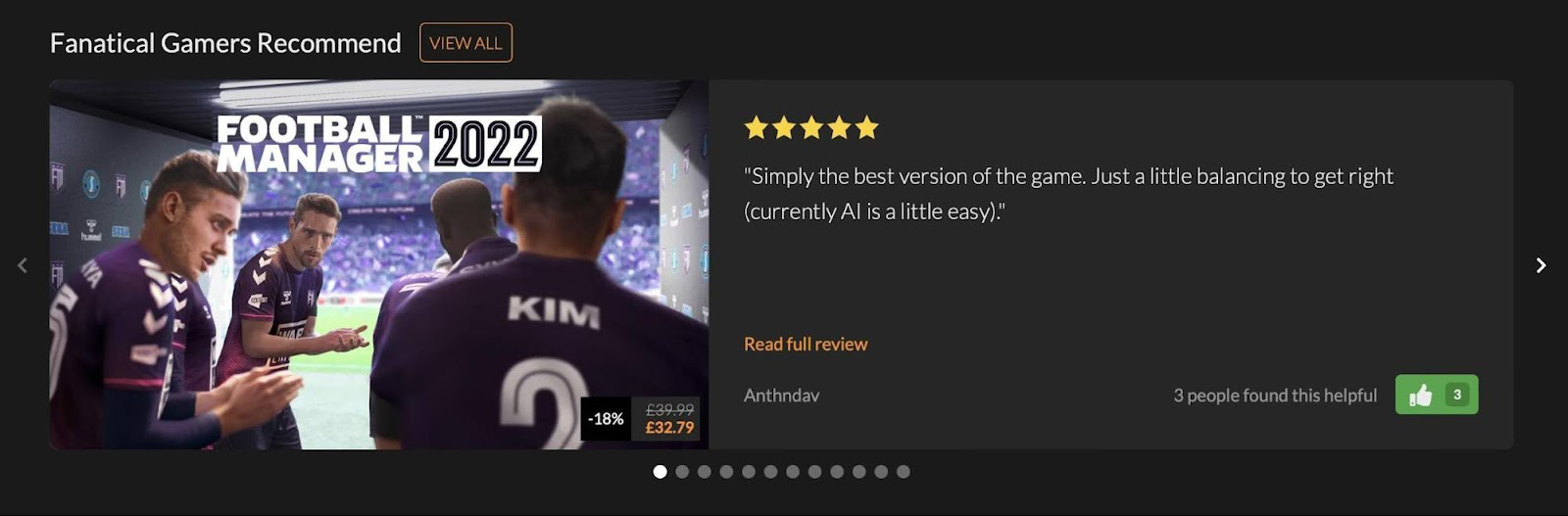
7. Reviews
According to Reevoo, positive reviews can increase profits on average by 18% and, therefore, deserve special attention. On many sites, leaving reviews on the product card is impossible. Thus you can use the category pages for this purpose.
The Fanatical online store is a good example.
On this resource, you can find players' recommendations in each category. Games with good reviews get high PageRank, are well ranked, and converted.
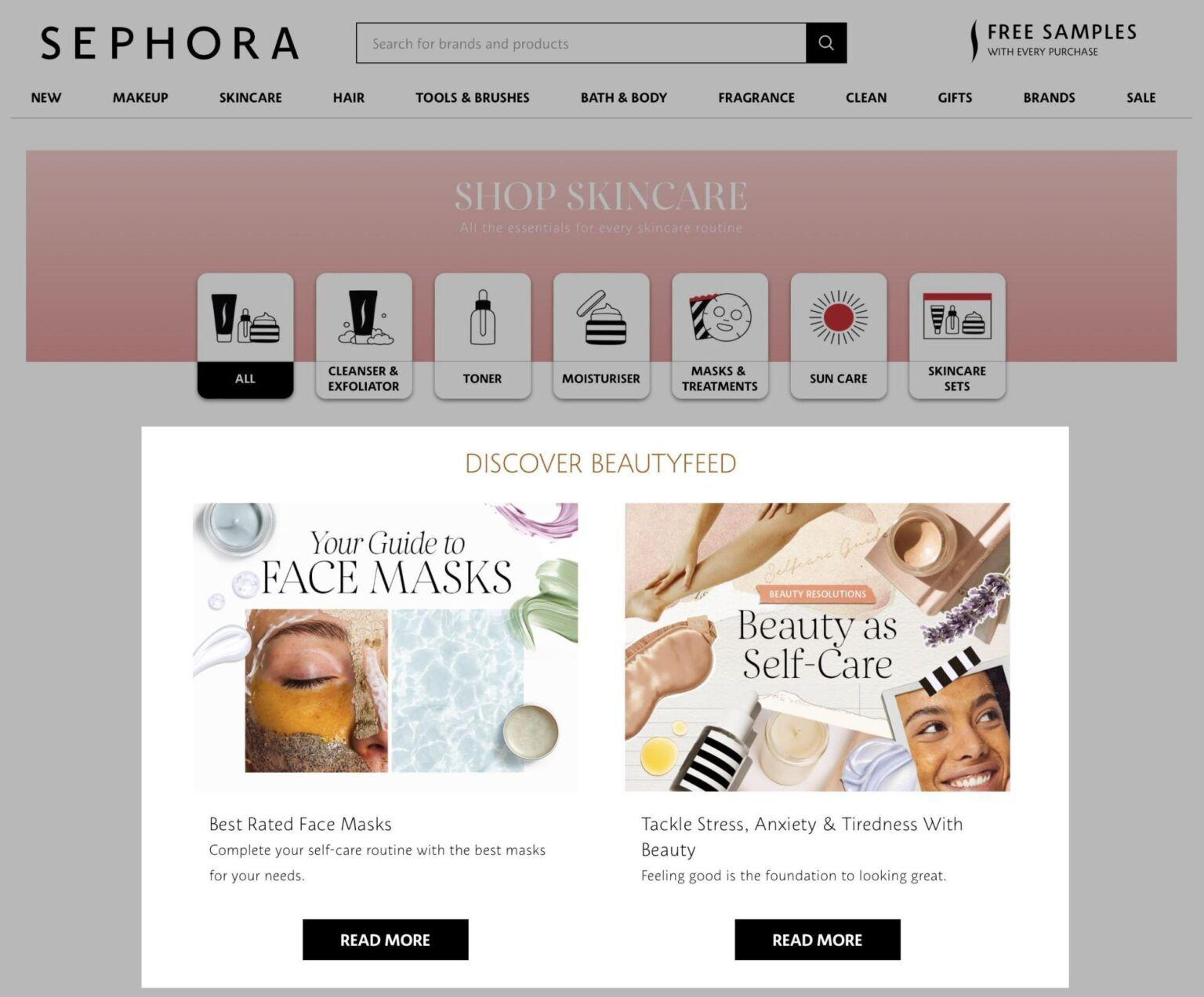
8. Helpful articles and tools
Publish expert content on your blog that answers the user's questions and works on your brand's reputation, and refer to it on the category pages.
See how this idea is implemented on the Sephora website.
The pages of the site's categories contain links to materials, the purpose of which is to help buyers choose goods. This approach allows you to promote specific products and improves the ranking of the blog pages. In addition, if the resource contains a large amount of related content, Google will assess your expertise in the topic.
9. Optimal URL structure
As for the URL structure, experts give a lot of practical advice. Above all, however, one should choose a structure that does not have to be modified. Changing a URL makes indexing more complicated and risky and should not be repeated unnecessarily. The reasons for change may include rebranding.
Page addresses of categories should be simple and humane, and their change should be planned. For example, you can instruct developers to structure URLs by generic links between categories.
www.example.com/mens/
www.example.com/mens/trainers/
www.example.com/mens/trainers/white/
For example, if you sell sneakers and want to expand the shoes range, most likely, you will add “Shoes” as the main category to the subcategory of “Trainers” and create a new “Boots” page within it.
URL addresses will look like the following:
www.example.com/mens/
www.example.com/mens/shoes/
www.example.com/mens/shoes/trainers/
www.example.com/mens/shoes/trainers/white/
www.example.com/mens/shoes/boots/
This approach involves setting up a redirection for the “Trainers” URL and any subcategories it has.
However, remember that the simpler the structure, the less change will be required. For example, if you take a top-level category for a ”white trainers” URL and then add the last one, the page address will be displayed as follows:
www.example.com/mens/white-trainers/
URL will remain unchanged if you change any higher categories for the “White Trainers”. However, this is not true for breadcrumbs. So the question is, wouldn’t it be better to make the structure as simple as possible so that the page address looks like this:
www.example.com/mens-white-trainers/?
Experience shows that structured URLs improve ranking. At the same time, do not forget about the risks associated with changing the address, when choosing your approach to forming URLs.
10. Title tags and H1s
Work on the title and H1 tags should start with keyword research and selection, with which potential buyers can look for your products. Use general tips for a successful title selection.
Use the title templates corresponding to the H1 content. In 2021, due to a change in the basic algorithm, Google began to show meta tags H1 or even H2 instead of titles.
According to Ahrefs, the search engine rewrites the title in 33.4% of cases. If the title differs from H1, Google changes it to H1 50.76% of the time, 2.02% to H2, and 1.31% to H1 and H2. The rest 45.91% is other content received from the website pages.
Templates such as: [Page H1] - [Brand Name] can guarantee the search engine won’t make changes. You may want to change the page title. The most effective option should be chosen based on the results of testing.
Here are some test examples:
- use «–» instead of «|»;
- add a price [Page H1], starting from X — [Brand Name];
- add “buy” at the start of title — buy [Page H1] — [Brand Name];
- include secondary keywords — [Page H1] — [Secondary Keyword] — [Brand Name].
In addition, it is possible to check the size of the header. With a 57% probability, Google will rewrite the title with a volume exceeding 600 px (50-60 characters).
11. Structured data
To help Google better understand the website content, you can add structured data types to the category pages, such as:
- breadcrumb;
- FAQ.
The placement of such information has a direct impact on the SERP snippet.
In the latter case, structured data is added in the Schema.org validator:
Google suggests using only the specified types of structured data on category pages. However, don’t limit yourself to these recommendations.
As for additional structured data, according to Google software engineer Ryan Levering, such elements can be helpful when the search engine has difficulty understanding the page content. However, such cases are sporadic. It means that additional structured data is still a secondary area.
At the same time, the following tools are worth mentioning:
- CollectionPage is more specific compared to WebPage;
- ItemList informs Google that there is a list of elements on the page.
You can add mainEntity to the tools mentioned above. With this app, the search engine understands that the page is a specific category because it contains a list of goods.
Here is a simple example of what this might look like:
{
"@context": "http://schema.org",
"@type": "CollectionPage",
"mainEntity": {
"@type": "ItemList",
"numberOfItems": "[number of products]",
"itemListElement": [
{
"@type": "ListItem",
"position": 1,
"url": "[Item URL]",
"name": "[Item Name]"
},
{
"@type": "ListItem",
"position": 2,
"url": "[Item URL]",
"name": "[Item Name]"
},
{
"@type": "ListItem",
"position": 3,
"url": "[Item URL]",
"name": "[Item Name]"
}
]
}
}
Professional advice
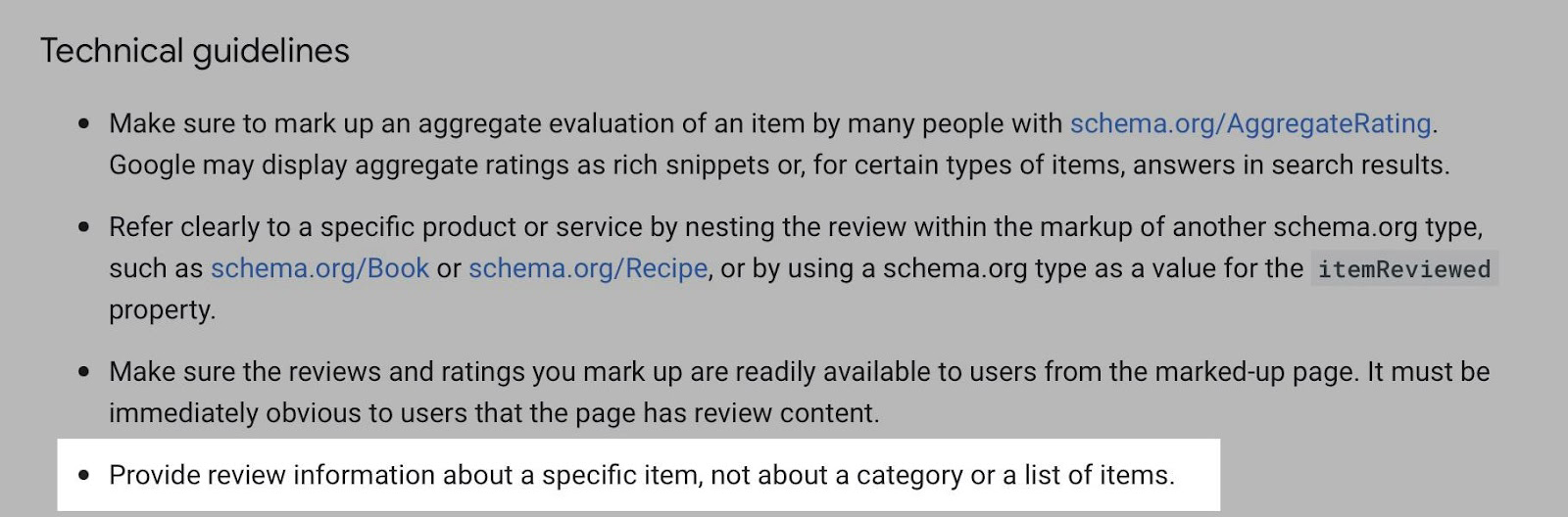
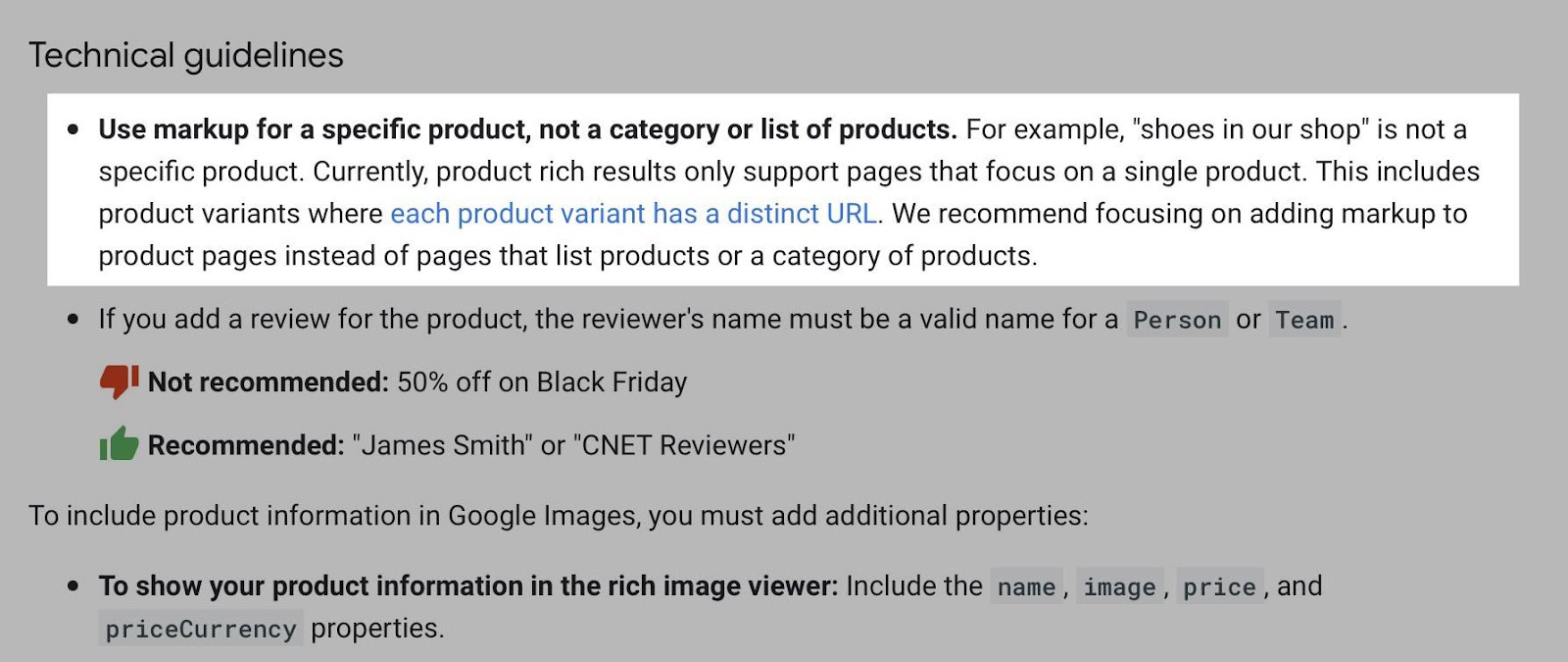
You may have noticed no mention of markup in the article. Even though some online stores add it to the category pages, do not do this.
By the way, Google, in the technical guidelines, also does not recommend applying markup on pages that contain mainly list elements.
Google also provides such instruction on the product pages' structured data.
Summary
Applying the above tips in practice, you can significantly improve the usability of your resource's pages and make them effective in terms of SEO. However, remember that such detailed work is impossible without knowledge of Google's promotion and algorithms nuances, so entrusting it to an experienced team is advisable. Contact our eCommerce SEO agency; we will help you optimize your website pages and increase conversion and sales.
We care about improving your sales :)